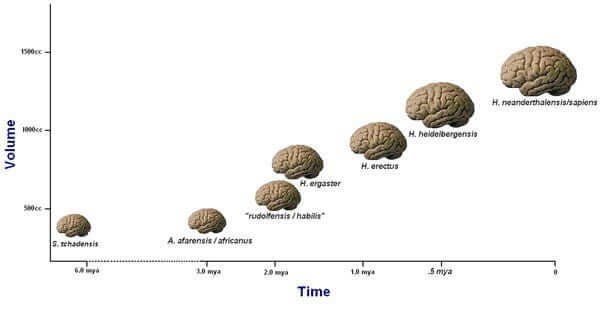
The modern human brain, as we know it, evolved as early as 1.7 million years ago in Africa. It’s relatively young.
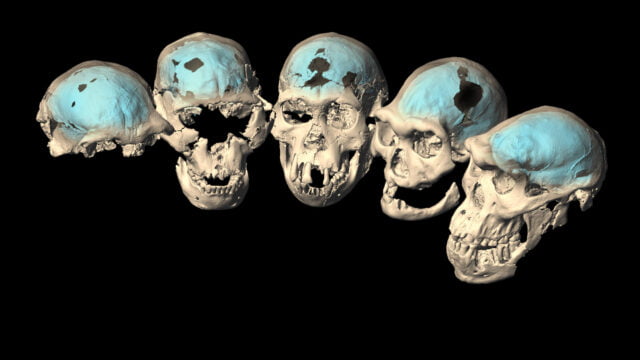
At a time when the complexity of tools made out of stone was widespread, the human brain underwent a massive evolution.
After researching fossilized skulls (not as scary as it sounds), using computed tomography analyses, researchers found shreds of evidence to suggest that not much later, the new man with the new brain started inhabiting Southeast Asia.
Tracing The Earliest Human Brain
As compared to our closest relatives known as of yet, The Great Apes, we are fundamentally different in varying aspects.
We walk on two legs, they generally don’t. We walk on the grounds, they usually prefer much higher areas. We have larger brains, they have relatively tiny.
The first Homo population was seen in Africa about 2.5 million years ago. This set of Homo walked on two legs, but the size of their brain was half as that of ours.
Their brains had more in common with primitive apes than modern humans, like their ancestor’s Australopithecines.
Emergence Of The Modern Brain Structures
A specialized team from the Department of Anthropology at the University of Zurich (UZH), led some CT scans that led them to believe that the “modern human brain structures emerged only 1.5 to 1.7 million years ago in African Homo populations.“
Computed tomography was put in use to scan the fossilized skulls of the Homo population residing in Africa and Asia.
After sufficient data was collected, they cross-referenced it to that collected from the great apes and humans.

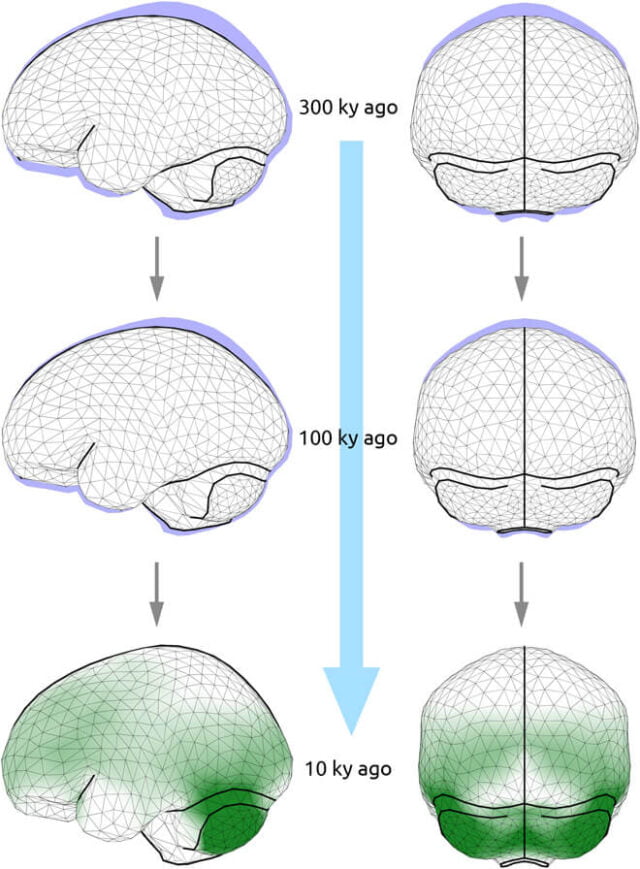
Regarding the location and organization of individual brain regions, the human brain has been observed to vary greatly from the brain of the great apes.
According to the team mentioned above, “The features typical to humans are primarily those regions in the frontal lobe that are responsible for planning and executing complex patterns of thought and action, and ultimately also for language.”
Read More: Can Hacking The Human Brain Make Us Smarter?
The Spread Of The Modern Human Brain
The initial Homo population had a brain that was as primitive as its African relatives and around 1.7 million years ago, evolution saw the light of the day.
Despite evolving into the modern brain, these Homo could adjust and become capable of making tools, adapting to environmental conditions (however unfavorable), and living as a big family that cared for each of its members.
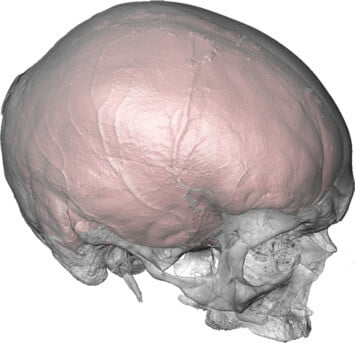
By that time, Africa saw numerous biological and cultural evolutions alike and researchers strongly believe that “the earliest forms of human language also developed during this period.”
The success of these populations has been based on fossils found in Java.
Looking At Brain Imprints
Brain imprints are of utmost significance since “the brains of our ancestors were not preserved as fossils. Their brain structures can only be deduced from impressions left by the folds and furrows on the inner surfaces of fossil skulls.”
Moreover, the variation itself varies from person to person which points to the mere possibility of finding out whether a fossil had a close relation to ape-like, or human-like brain.
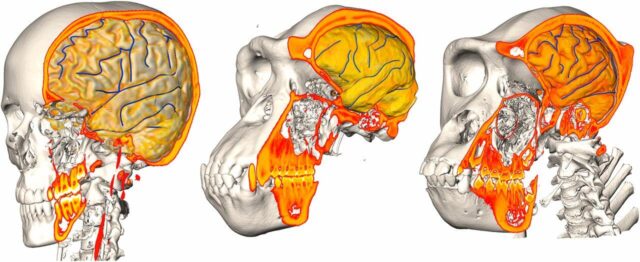
Thanks to computed tomography analyses, the lines between oblivion and proof have become less blurry due to the hard work of researchers working night and day.
We finally have data enough to trace the modern human brain back to 1.7 million years ago.
Image Source: Google Images
Sources: Republic World, Science Daily, Daily Mail
Find The Blogger: @evidenceofmine
This post is tagged under: human brain, modern human brain, evolution, evolved human brain, Africa, stone tools, fossils, skull, human skull, fossilized skull, tomography, computed tomography analysis, research, researcher, Southeast Asia, the great apes, apes and humans, homo, homo sapiens, human ancestor, human ancestry, Australopithecus, australopithecines, modern brain structure, Department of Anthropology, anthropology, CT scans, human brain CT scan, language, culture, human brain structure, primitive human brain, primitive man, fossils in Java, Java, human fossils, brain imprints, brain furrows, brain folds, what are brain imprints, how did the human brain evolve, when did the human brain evolve, tracing the modern human brain

































